A Women’s Worst Nightmare
Women get breast cancer more often. One in eight American women will get invasive breast cancer.
These statistics are alarming, but it’s important to remember that not all breast lumps are cancerous. Most breast lumps are benign and not life-threatening. But not to worry there are different types of stage 1 breast cancer treatment to become healthy again.
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection is crucial to breast cancer therapy.
This means that women must be proactive about monitoring their health by performing monthly self-exams and getting regular mammograms as their doctor recommends.
Early discovery improves prognosis and survival. Women should be aware of breast cancer symptoms including a lump or thickening in the breast tissue, changes in breast size or form, nipple discharge other than breast milk, and swelling or redness around the nips.
These symptoms need emergency medical attention.
Early diagnosis via monthly self-exams and mammograms improves survival rates and outcomes for breast cancer, which affects many women throughout their lives.
Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Definition and Features
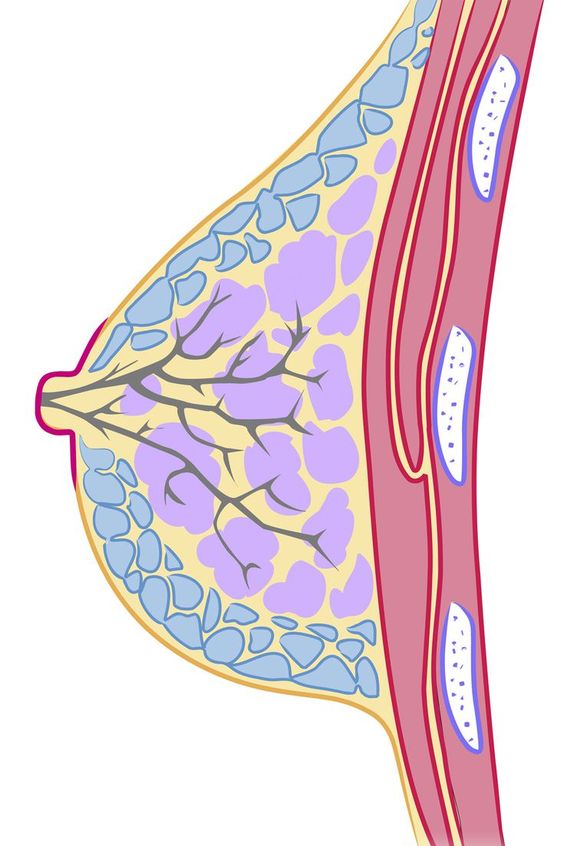
Early breast cancer is stage 1. Stage 1 breast cancer has a tumor under 2 cm and has not spread to surrounding tissue or lymph nodes. Even within stages, breast cancers vary.
Different breast cancers demand different therapies. Stage 1 breast cancer includes DCIS.
This type of cancer involves abnormal cells in the milk ducts but has not yet invaded nearby tissue. Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) starts in the milk ducts and spreads to nearby tissue.
Diagnosis Process
Early detection through regular mammograms and self-exams can lead to early stage 1 breast cancer diagnosis. A biopsy will identify whether a tumor or growth is cancerous.
The biopsy involves taking a small tissue sample from the affected area using a needle or surgical removal. whether the biopsy shows malignant cells, more testing may be needed to establish whether the tumor has spread.
These tests may include imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan and additional biopsies of surrounding lymph nodes. Once a diagnosis of stage 1 breast cancer has been confirmed and further testing has ruled out any spreading beyond its initial site, their healthcare team will discuss treatment options with the patient.
Surgery: How do they treat stage 1 breast cancer
Lumpectomy vs. Mastectomy
Treatment breast cancer stage 1 therapy includes surgery. The tumor size, location, and personal choice determine the procedure.
A lumpectomy removes only the tumor and some surrounding tissue, while a mastectomy removes the entire breast.
Some women want a lumpectomy to retain their breast tissue and body image, while others prefer a mastectomy to decrease the chance of recurrence or hereditary susceptibility to breast cancer. Before choosing, talk to your doctor and ask questions.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is commonly done after a lumpectomy or mastectomy to evaluate whether the cancer has spread.
This involves injecting a dye into the area around the cancer, which travels through your lymphatic system to your sentinel nodes. These are typically the first lymph nodes affected if cancer spreads outside your breast.
The surgeon will then remove these sentinel nodes and send them to be analyzed to determine if any signs of cancer are present. If there isn’t, no further surgery will likely be required.
Radiation Therapy
Purpose and procedure: Stage 1 Breast Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is another standard treatment breast cancer stage 1. It uses high-energy radiation targeted at specific areas to destroy any remaining cancer cells after surgery or shrink tumors before surgery.
During radiation therapy, you’ll lie on a table while a machine delivers precise doses of radiation into your body over several sessions. The number of sessions can vary depending on age, health status, and type of tumor being treated.
Side effects
While radiation therapy can be highly effective, it has potential side effects. Fatigue, skin irritation and redness in the treatment region, breast edema, and breast texture or color changes might occur.
These negative effects will subside with time.
Your doctor may recommend creams or other treatments to help manage any discomfort you experience.
Chemotherapy: Effective Treatment Breast Cancer Stage 1
When it is necessary
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout your body. It’s typically used for more aggressive forms of stage 1 breast cancer or when there’s a higher risk of recurrence. Your doctor will consider factors such as tumor size and grade, hormone receptor status, and genetic testing results when determining if chemotherapy is necessary for you.
Types of drugs used
Several different types of chemotherapy drugs may be used depending on your situation. Some standard options include anthracyclines, taxanes, and cyclophosphamide.
The specific drugs chosen may also depend on factors such as age, other health conditions, and any previous treatments you’ve received. Your doctor will create a treatment plan based on these criteria.
Hormonal Therapy
How it works
Hormonal therapy involves taking medications that block the production or action of certain hormones in your body. This can effectively treat stage 1 breast cancer since some types of tumors rely on hormones like estrogen to grow and spread. Hormonal treatment may include SERMs, AIs, or other medicines, depending on a woman’s age and hormone receptor status.
Side effects
Most hormonal therapy may cause hot flashes, mood disturbances, vaginal dryness, and osteoporosis. Some women may also get blood clots or other cancers.
Despite these dangers, hormone therapy reduces stage 1 breast cancer recurrence in many people. Your doctor can help you balance the advantages and downsides and choose this therapy.
Follow-up Care
The diagnosis and treatment of stage 1 breast cancer are not the end of the journey. Regular follow-up treatment reduces recurrence and metastatic risk.
Follow-up treatment includes doctor visits, mammograms, blood tests, chest X-rays, and bone scans. Age, medical history, general health, and therapy determine follow-up frequency and kind.
Doctors will check for recurrence and metastases during follow-ups. Persistent breast or underarm discomfort, swelling or lumps, skin texture or color changes around the breasts or nipples, unexplained exhaustion, or weight loss are frequent symptoms.
However, it’s important to note that many recurrences only produce symptoms once they are advanced. That is why regular check-ups are so crucial.
Monitoring for Recurrence or Metastasis
Doctors may use different imaging tests to monitor for recurrence or metastasis after stage 1 breast cancer treatment. Mammography is usually done every year for at least five years after treatment. MRI may be used if there is uncertainty about suspicious areas found on mammography testing.
A mastectomy may be needed if further testing reveals that cancer has returned (a local recurrence) in a woman who had a lumpectomy but no radiation therapy after surgery. In some cases, when some women have received radiation therapy after a lumpectomy and then have another breast cancer found later (not necessarily another new primary), they can undergo another lumpectomy if both cancers (the original plus the new one) can be removed with clear margins by using larger margins than typical around each tumor bed; however, these patients need close monitoring because their risk of yet another developing yet another new primary cancer in that same breast over time is increased.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk Factors
In stage 1 breast cancer treatment survivors, confident lifestyle choices may minimize the chance of recurrence or metastasis. This involves keeping a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising frequently, limiting alcohol, avoiding cigarettes, and managing stress. Studies show that women who exercise after breast cancer diagnosis live longer and have a decreased chance of recurrence.
Most days, exercise moderately for 30 minutes. Healthy eating and exercise are key.
Eat plenty of healthy grains and vegetables.
Avoid processed foods and red meat.
Limit sugar-sweetened drinks like soda or sweet tea. Obesity raises the risk of cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
– managing stress is also essential when dealing with any chronic health condition – including breast cancer. Participating in activities such as yoga or meditation can help you relax and cope with uncertainty during follow-up care visits.
FAQ
What is the stage 1 breast cancer treatment timeline?
How do you treat stage 1 breast cancer?
How is stage one breast cancer treated?
What is the typical treatment for stage 1 breast cancer?
Conclusion
Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for a positive outcome in stage 1 breast cancer treatment patients. It is essential to perform regular self-examinations, follow up with your doctor regularly, and get mammograms as your healthcare provider recommends.
Contact your doctor immediately if you suffer breast changes, nipple discharge, or lumps.
The good news is that stage 1 breast cancer has a high survival rate when detected early.
There is hope for complete remission with appropriate treatment options such as surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy available for stage 1 breast cancer patients. A balanced diet and regular exercise may also lessen the chance of cancer recurrence.
Receiving a stage 1 breast cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming and scary. However, with the right attitude and support system in place, along with current advancements in technology and medicine available today – we can all remain positive, knowing that proper detection and treatment will allow us to live long, fulfilling lives beyond our diagnoses.

Leave a Reply